平方根
求解一个数的平方根
牛顿迭代法
牛顿迭代法就是使用切线不断逼近目标值
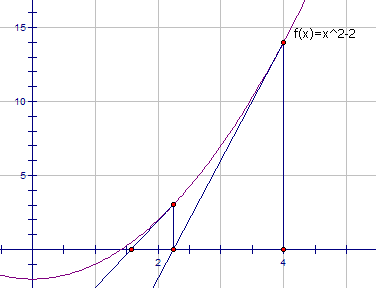
设一个函数 f(x) = x^2 - a ,该函数与x正半轴的交点就是a的平方根 a^(1/2)
使用取一个点让该函数的切线不断靠近该点 函数的切线斜率易知是 2x 方程为y = 2x(x - b)
然后求该切线的截距 可得 b = x - f(x) / 2x 将f(x) 带入 化简得 b = (x + a /x) / 2
让切线不断逼近a,所以最后 近似a^(1/2) = b = (x + a /x) / 2 就可以近似求出a 的平方根
1
2
3
4
5
| public static int mySqrt(int a) {
int x = a;
while(x * x > a) x = (x + a / x) / 2;
return x;
};
|
树
二叉树
前序遍历
遍历顺序: 根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树 (中 左 右)
递归法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static List<Integer> before(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
digui(root, res);
return res;
}
public static void digui(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if(root == null) return;
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.left, res);
inorder(root.right, res);
}
|
迭代法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while(root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while(root != null) {
stk.push(root);
res.add(root.val);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
|
中序遍历
遍历顺序: 左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树 (左 中 右 )
递归法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static List<Integer> midlle(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
digui(root, res);
return res;
}
public static void digui(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if(root == null) return;
inorder(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, res);
}
|
迭代法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public static List<Integer> middle(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while(root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while(root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
|
后序遍历
遍历顺序: 左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点 (左 右 中 )
递归法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static List<Integer> after(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
digui(root, res);
return res;
}
public static void digui(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if(root == null) return;
inorder(root.left, res);
inorder(root.right, res);
res.add(root.val);
}
|
迭代法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while(root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while(root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
if(root.right == null || root.right == pre) {
res.add(root.val);
pre = root;
root = null;
}
else {
stk.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
|

